If you’ve heard of Bitcoin, you’ve probably heard of cryptocurrency mining. But 15 years after Bitcoin was created, the term has become shrouded in myth.
In simple terms: Mining is the heartbeat of the Bitcoin network. It is a process that not only creates new coins, but also ensures the security of the entire system. Without miners, Bitcoin would cease to exist and transactions would stop forever.
In 2025, mining has changed. It is no longer a hobby for geeks with laptops, but a global industry that helps stabilise power grids and uses renewable energy. In this article, we will explain in simple terms what Bitcoin mining is, how it works on a technical level, and why it is important for the future of finance.
There are a lot of companies like GoMining who provides mining services
What is cryptocurrency mining?


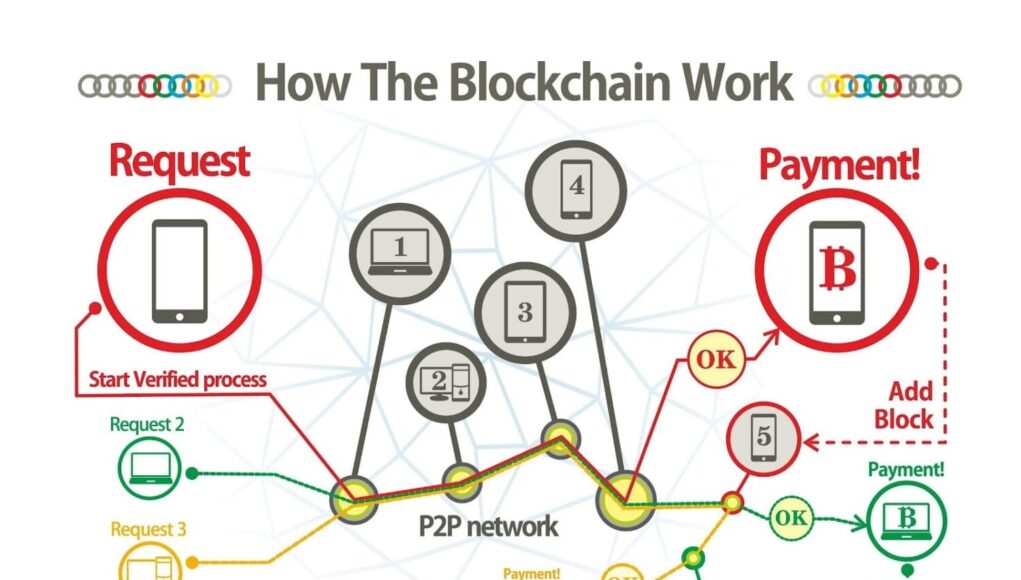
Imagine that Bitcoin is a huge shared digital notebook (blockchain) in which every money transfer is recorded. Since Bitcoin has no bank or boss, someone has to make sure that no false entries are made in this notebook.
This is what miners do.
Cryptocurrency mining is a global competition between powerful computers. Their task is to solve a complex mathematical puzzle.
- Computers around the world compete to see who can solve the puzzle first.
- The winner gets the right to add a new ‘page’ (block) with entries to the shared notebook.
- As a prize, the winner receives a reward for the block and transaction fees.
It’s a brilliant system: miners spend electricity and resources to protect the network, and the network pays them for their honesty.
Mini glossary for beginners
- Miner: A computer that performs the work of verifying transactions.
- Block: A group of transactions compressed into a single digital file.
- Hash: A unique digital fingerprint of a block.
- Difficulty: A parameter that determines how difficult it is to find the correct hash.
- Proof-of-Work: A mechanism that requires energy expenditure to confirm transactions.
How Mining Works


Many people ask, ‘How does cryptocurrency mining work?’ Let’s break down the process step by step, like a science experiment.
Step 1: Transactions enter the ‘Waiting Room’
When you send Bitcoin to a friend, the transaction does not go through instantly. It goes into the Mempool (memory pool) — a kind of waiting room where transactions wait to be confirmed.
Step 2: Miners collect transactions into a box
Miners select transactions from the Mempool and pack them into block candidates. They usually choose transactions with the highest fees to earn more.
Step 3: Competition
This is the most important part. To add a block to the network, a miner must find a unique code (hash) for that block.
- Analogy: Imagine you have a million dice. You need to roll them so that the sum of the numbers is less than a certain value. The chance of doing this on the first try is one in a billion.
- Miners make trillions of attempts per second. This is called the hash rate.
Step 4: The winner announces the result
As soon as one miner in the world finds the correct solution (the ‘golden hash’), they broadcast it to everyone else. Other miners quickly verify: ‘Yes, the solution is correct.’
Step 5: Reward and new cycle
The block is added to the blockchain. The winning miner receives a reward. In 2025 (after the 2024 halving), it will be 3.125 BTC plus user fees. The race immediately starts again for the next block.
Types of mining equipment
Cryptocurrency mining equipment has come a long way. What worked in 2010 is useless today.
1. CPU mining — Obsolete
In the early days, Bitcoin could be mined on a regular laptop. Today, the difficulty is so high that it would take millions of years to find a single block using a processor.
2. GPU mining — For altcoins
Graphics cards are more powerful than processors. They were used for Bitcoin until 2013. Now GPUs are used for mining other coins or for artificial intelligence tasks, but for Bitcoin they are too weak and energy inefficient.
3. ASIC mining
What is an ASIC miner? It is an Application-Specific Integrated Circuit — a microchip designed for one single task: mining Bitcoins.
- They are thousands of times more efficient than regular computers.
- Examples from 2025: Antminer S21, Whatsminer M60.
- These are noisy, hot industrial machines that require special cooling.
Why is mining still important in 2025?
You may ask, ‘Why waste so much energy?’ Here’s why mining is important and why it won’t disappear.
1. Mining protects the network
This is the main function. The Bitcoin security model is built on the cost of an attack. To hack the network or rewrite the transaction history (51% attack), a hacker would need to control more computing power than all the miners in the world combined. In 2025, this would require billions of dollars in equipment and electricity, making the attack economically pointless.
2. Mining decentralises the network
There is no central server that can be shut down. Miners are scattered around the world, from Texas to Bhutan and Paraguay. This ensures that no government can ‘turn off’ Bitcoin.
3. Coin issuance
Bitcoins do not appear out of thin air. Mining is the only way to release new coins into circulation. This process is strictly controlled by code (inflation decreases every 4 years), making Bitcoin a scarce asset.
4. Censorship resistance
When China banned mining in 2021, the network did not stop for a second. Miners simply moved to other countries. How has mining changed over time? It has become an incredibly resilient and mobile business.
Why mining is still relevant in 2025
In 2025, cryptocurrency mining has become more deeply integrated into the global economy than ever before.
1. Stabilisation of energy grids
Miners have become the best friends of energy companies. They work as a ‘controlled load.’ When there is excess energy in the grid, miners turn on their equipment and buy cheap electricity. When demand increases, miners shut down, giving energy to cities.
2. Green mining and flared gas


The myth that mining ‘boils the oceans’ has been dispelled.
- Hydroelectric power: A huge portion of mining is powered by water (Canada, Norway, Bhutan).
- Flared gas: Miners install containers at oil fields, using gas that was previously simply burned into the atmosphere. This actually reduces the carbon footprint of oil production.
3. Institutional acceptance
Large investment funds and even countries (such as El Salvador and Bhutan) now own mining facilities. This makes the infrastructure more reliable.
Will crypto mining still be profitable in 2025?
The short answer: Yes, but not for everyone. Gone are the days when you could get rich with a single graphics card. Cryptocurrency mining in 2025 is a low-margin business.
What affects profitability:
- Electricity costs: This is the number one factor. If you pay more than $0.06 per kWh, mining Bitcoin will most likely be unprofitable.
- Equipment efficiency: Old ASICs consume too much energy. New models (S21, XP) are needed.
- Bitcoin price: The higher the price, the more profitable it is to mine.
- Network difficulty: The more miners there are, the more difficult it is to mine a block.
Profitability thermometer:
- Home mining: Usually unprofitable due to electricity rates and noise.
- Hosting: Moderate profit if you choose the right provider.
- Industrial mining: High efficiency due to wholesale energy prices.
Conclusion: Why mining will not disappear
After 15 years, we can say with confidence that cryptocurrency mining is not a passing fad. It is the foundation on which the entire digital asset industry stands.
As mining becomes more intertwined with the global financial system, many investors also analyse broader market tools — such as forex broker comparisons — to understand how traditional and crypto markets interact, hedge risk, or diversify exposure.
What is Bitcoin mining today?
- It is a shield that protects the savings of millions of people.
- It is a tool that helps develop green energy.
- It is a mechanism that guarantees honesty without intermediaries.
As long as there is a need for decentralised money that cannot be counterfeited or censored, miners will continue their work, solving the most complex puzzles and adding new pages to the blockchain’s history.
FAQ
- What is hashrate?
It is the total computing power of all miners in the network. The higher it is, the more secure the network is.
- How long does it take to mine 1 Bitcoin?
A single miner does not mine Bitcoin alone. They participate in a pool. On a powerful modern ASIC, mining 1 BTC can take years, but in a pool you get small portions of the reward every day.
- Does mining consume too much energy?
Mining consumes a lot of energy, but it increasingly uses surplus or renewable energy that would otherwise be wasted.
- What is a mining pool?
It is an association of thousands of miners who work together as one supercomputer and share the reward equally depending on each person’s contribution.
- What is the difference between Proof-of-Work and Proof-of-Stake ?
PoW requires energy expenditure for security . PoS requires coin locking . PoW is considered more reliable and decentralised.
- How can a beginner start mining?
The safest way in 2025 is to buy an ASIC and place it in a specialised data centre (hosting), or to buy shares in mining companies.