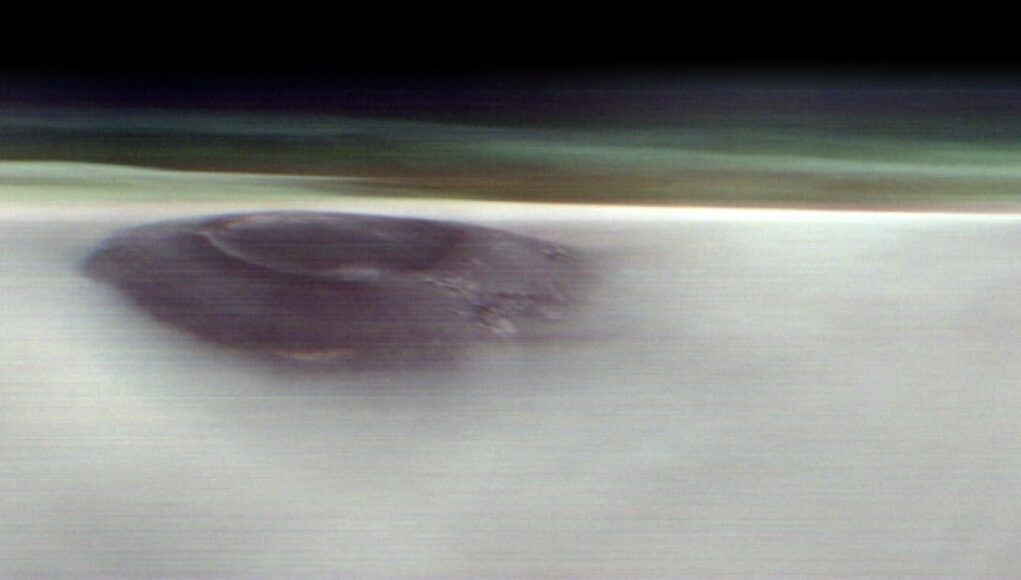
NASA’s longest-running Mars mission has sent back an unprecedented side view of a massive volcano rising above the Red Planet, just before dawn.
On May 2, as sunlight crept over the Martian horizon, the Odyssey spacecraft captured Arsia Mons, a towering, long-extinct volcano, puncturing a glowing band of greenish haze in the planet’s upper atmosphere.
The 12-mile-high volcano — nearly twice the height of Mauna Loa in Hawaii — punctures a veil of fog, emerging like a monument to the planet’s ancient past. The space snapshot is both visually arresting and scientifically enlightening.
“We picked Arsia Mons hoping we would see the summit poke above the early morning clouds,” said Jonathon Hill, who leads Odyssey’s camera operations at Arizona State University, in a statement, “and it didn’t disappoint.”

Arsia Mons sits at the southern end of a towering trio of volcanoes called the Tharsis Montes.
Credit: NASA / JPL-Caltech
To get this view, Odyssey had to do something it wasn’t originally built for. The orbiter, which has been flying around Mars since 2001, usually points its camera straight down to map the planet’s surface. But over the past two years, scientists have begun rotating the spacecraft 90 degrees to look toward the horizon. That adjustment allows NASA to study how dust and ice clouds change over the seasons.
Mashable Light Speed
Though the image is still an aerial view, the vantage point is of the horizon, similar to how astronauts can see Earth’s horizon 250 miles above the planet on the International Space Station. From that altitude, Earth doesn’t fill their entire view — there’s enough distance and perspective for them to see the planet’s curved edge meeting the blackness of space. Odyssey flies above Mars at about the same altitude.
Arsia Mons sits at the southern end of a towering trio of volcanoes called the Tharsis Montes. The Tharsis region is home to the largest volcanoes in the solar system. The lack of plate tectonics on the Red Planet allowed them to grow many times larger than those anywhere on Earth.
Together, they dominate the Martian landscape and are sometimes covered in clouds, especially in the early hours. But not just any clouds — these are made of water ice, a different breed than the planet’s more common carbon dioxide clouds. Arsia Mons is the cloudiest of the three.
Scientists have recently studied a particular, localized cloud formation that occurs over the mountain, dubbed the Arsia Mons Elongated Cloud. The transient feature, streaking 1,100 miles over southern Mars, lasts only about three hours in the morning during spring before vanishing in the warm sunlight. It’s formed by strong winds being forced up the mountainside.
The cloudy canopy on display in Odyssey’s new image, according to NASA, is called the aphelion cloud belt. This widespread seasonal system drapes across the planet’s equator when Mars is farthest from the sun.
This is Odyssey’s fourth side image since 2023, and it is the first to show a volcano breaking through the clouds.
“We’re seeing some really significant seasonal differences in these horizon images,” said Michael D. Smith, a NASA planetary scientist, in a statement. “It’s giving us new clues to how Mars’ atmosphere evolves over time.”